Demystifying TStore: The Backbone of Billions of Transactions at PhonePe
Disclaimer: The details in this post have been derived from the PhonePe Engineering Blog. All credit for the technical details goes to the PhonePe engineering team. The links to the original articles are present in the references section at the end of the post. We’ve attempted to analyze the details and provide our input about them. If you find any inaccuracies or omissions, please leave a comment, and we will do our best to fix them.
Ever Wondered How Your PhonePe Payment Happens in a Flash?
Imagine you’re at a grocery store, waiting in line to pay for your items. You scan the QR code with your PhonePe app, tap to pay, and within seconds, you see the green confirmation screen. Your transaction is complete, and the details are instantly updated in your transaction history. But have you ever wondered how this seamless experience is supported behind the scenes? Welcome to the world of PhonePe’s Transaction Store (TStore), the backbone that powers billions of transactions every day.
The Scale of PhonePe’s Transactions
PhonePe has been the leading third-party Unified Payments Interface (UPI) payment app in India. In August 2024, PhonePe alone recorded a staggering 7.23 billion customer-initiated UPI transactions, amounting to Rs 10,33,264.34 crore. To put that into perspective, this converts to roughly 124.49 billion USD for a single month. Extrapolating this for a year, PhonePe processes an incredible volume of transactions, highlighting the need for a robust and efficient system like TStore.
Unveiling TStore
The Backbone of Billions of Transactions
TStore is the unsung hero behind PhonePe’s seamless payment experience. It ensures high-velocity ingestion, efficient data retrieval, and real-time reads, powering billions of transactions every day. Let’s dive into how TStore makes this possible.
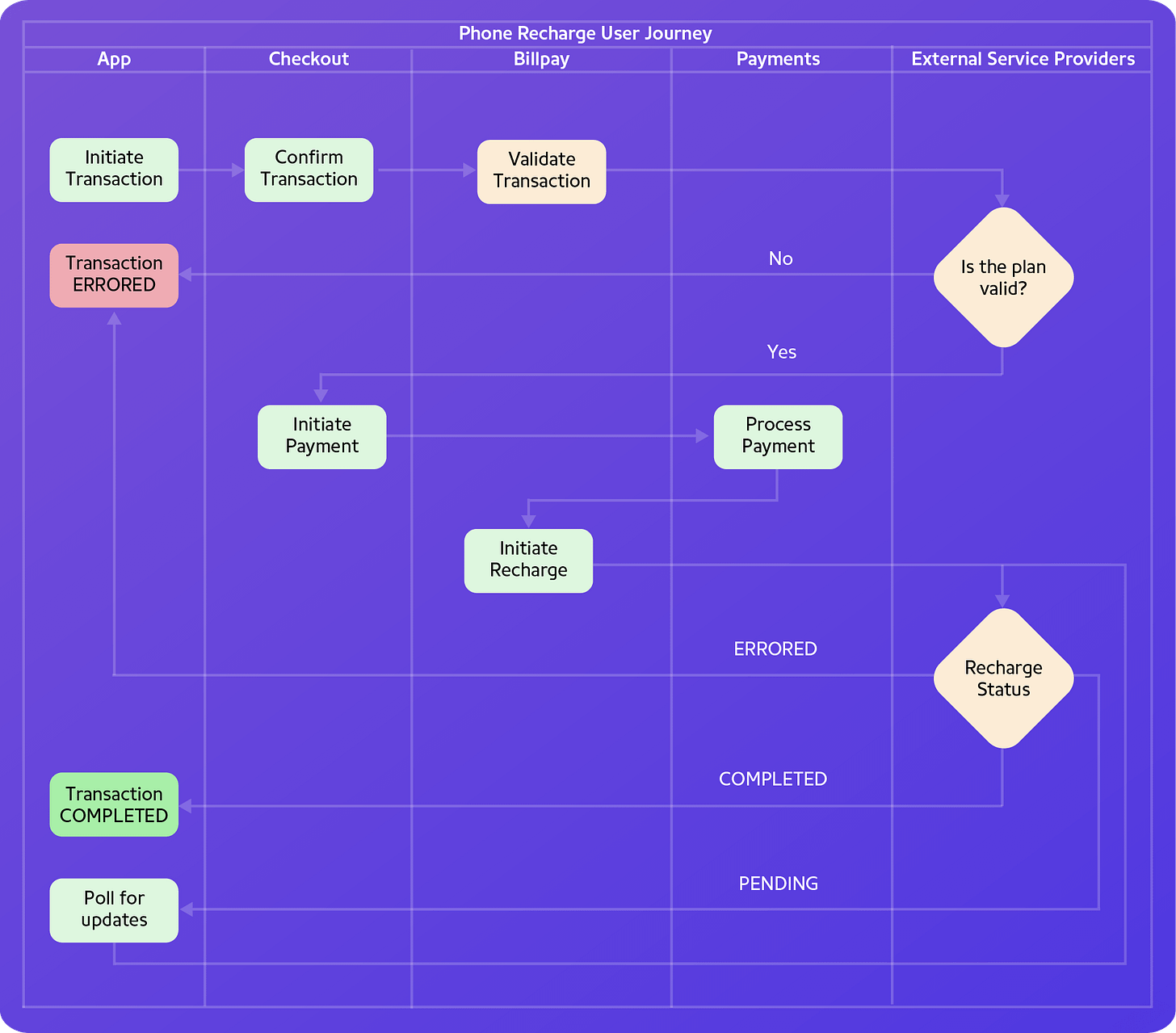
Capturing the User Journey
Consider a typical mobile recharge flow. You select a plan and top up your phone through PhonePe. Here’s a simplified view of how it works:
Initiate Recharge: You start the mobile recharge process through the PhonePe app.
Retrieve Payment Options: The Checkout Service fetches available payment options from BillPay.
Select Payment Method: You choose your preferred method (UPI, card, etc.) and submit payment details.
Validate and Initiate Transaction: The Payments Service validates constraints, initiates the transaction with the provider, and triggers fulfillment via BillPay.
Track Transaction Status: The app tracks the transaction status using TStore’s APIs, showing “PENDING” during processing and “COMPLETED” or “ERRORED” at the end.
TStore captures, consolidates, and disseminates payment flow information to stakeholders, ensuring a consistent post-payment experience.
Capabilities: High-Velocity Ingestion, Reads and Beyond
High-Velocity Ingestion: During peak hours, PhonePe processes over 8,000 transactions per second. TStore ingests data with minimal latency (~45,000 RPS and < 10 ms).
Efficient Scrolling Through Transaction History: TStore uses pointer-based scrolling mechanisms for efficient transaction retrieval:
Backward Scrolling for Initial Load: During initial app installation or when a user first accesses their transaction history, the client app downloads transactions in descending order of update timestamps.
Forward Polling for Updates: Apps already installed use forward polling to retrieve only the new updates that have occurred since the last poll, minimizing data transfer and improving response times.
Real-Time Reads: Both internal applications and external services rely on TStore for real-time access to transaction data, enabling features like instant transaction status and updates tracking (~100,000 RPS and < 20ms).
Flexible Querying Capability: TStore empowers diverse stakeholders with the ability to query and retrieve specific transaction details efficiently via real-time data aggregation, filtering, and sorting capabilities.
Historical Archiving Beyond Real-Time: TStore integrates with the data lake, enabling long-term storage and sophisticated analytics. This empowers deeper understanding of user behavior, payment trends, compliance reporting, fraud detection, and business insights.
Data Consistency and High Availability: TStore ensures data consistency across the system, spread across geographies, and implements redundancy, replication, and disaster recovery mechanisms to prevent service disruptions, ensuring business continuity seamlessly.
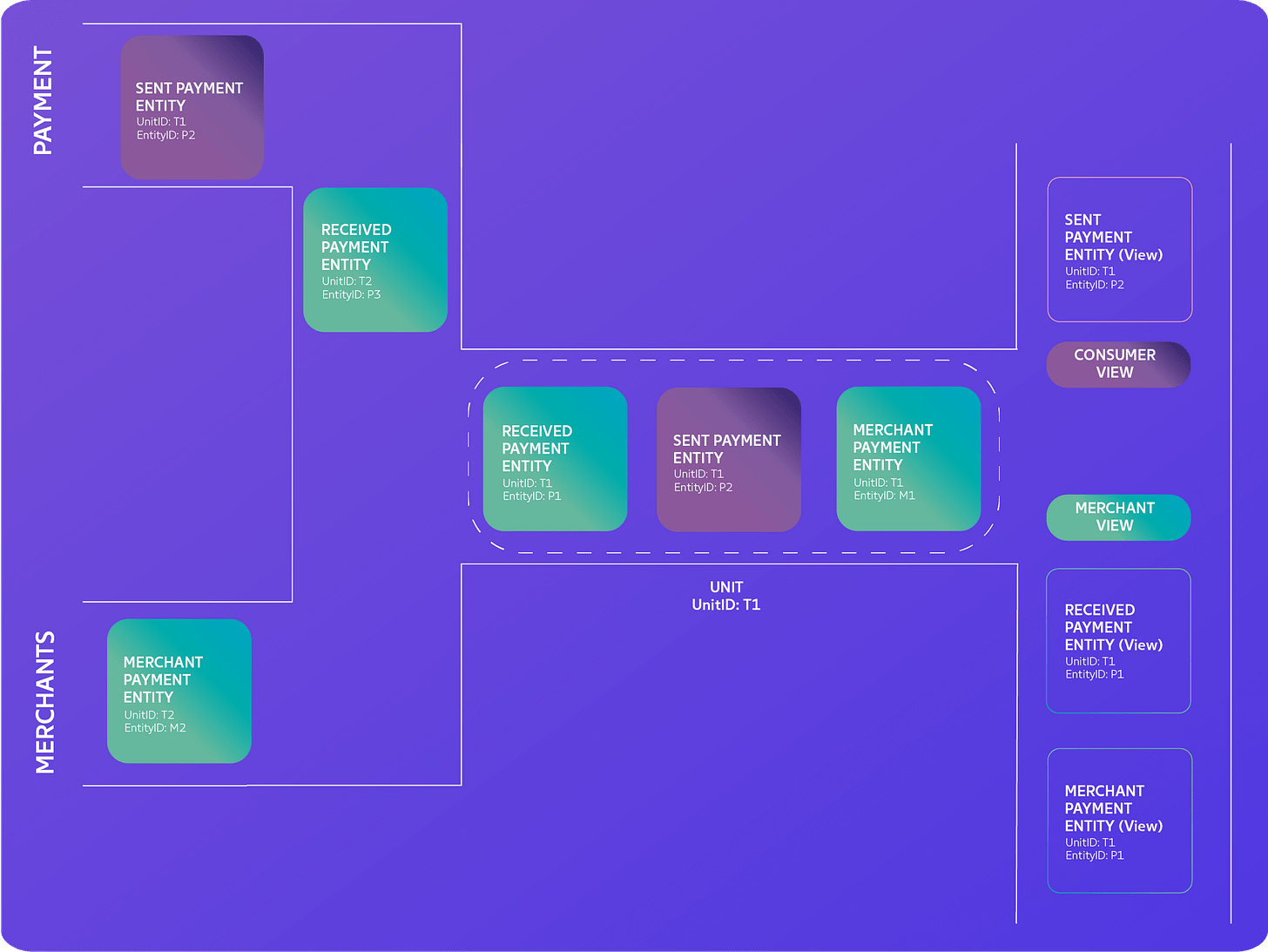
Terminologies
Entity: The most atomic element in TStore, representing actions taken by the user or supporting data elements generated by systems.
Unit: All entities are united by a common ID called Unit Id, consolidating their information, states, and timestamps into a unified record.
Views: Customizable filters applied to Unit details, ensuring clients only see relevant information, protecting privacy, and improving network efficiency.
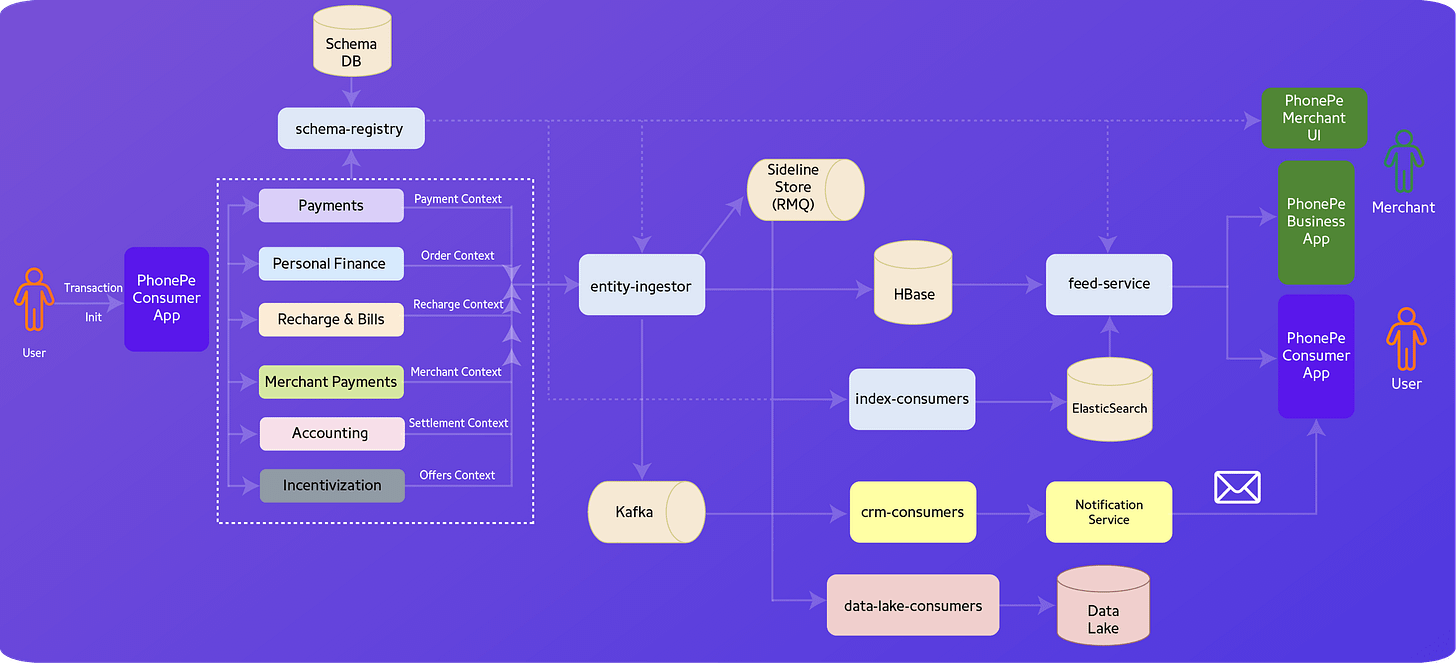
Architectural Deep Dive – A Closer Look at its Key Components
TStore Client Bundle: This library serves as the bridge between applications and TStore, abstracting away complexities, interacting with the discovery service, and ensuring serialized writes and maximized performance.
Schema Registry: Manages and governs the evolution of entity schemas within TStore, ensuring data integrity and facilitating seamless schema evolution.
Entity Ingestor: Responsible for ingesting new entities and disseminating updates across systems, ensuring data persistence and notification details are only sent if underlying data changes have been successfully persisted.
Feed Service: The primary gateway for read-only access to transaction data, enabling clients to poll for transaction status updates and providing paginated transaction history and dashboards for detailed analysis and reporting.
TStore’s Technical Foundations
1. Datastores: The Heart of TStore
HBase: The Transaction Backbone
HBase is TStore’s primary data store, chosen for its ability to handle high write throughput and ultra-fast reads. Here’s how it delivers:
Optimized Writes:
Data is written to an in-memory MemStore and a disk-based Write-Ahead Log (WAL).
These mechanisms minimize disk I/O, ensuring consistent performance even under heavy write loads.
Bloom Filters:
Bloom filters efficiently check if a row exists, speeding up index lookups for new transactions.
In-Memory Read Optimization:
Most reads target recently written data in MemStore, bypassing the disk.
For older data, block caching keeps frequently accessed SSTable blocks in memory, ensuring low-latency retrieval.
Cluster Architecture:
HBase operates on hundreds of Region Servers layered on HDFS (Hadoop Distributed File System).
This architecture enables fault tolerance and horizontal scalability, critical for managing billions of transactions.
HBase isn’t just fast—it’s resilient, offering fine-grained control over reads and writes. However, TStore remains adaptable to future datastore options, with compatibility for alternatives like Azure CosmosDB for scenarios requiring fully managed, globally distributed databases.
Elasticsearch: Search and Analytics Engine
While HBase excels at storing raw transactional data, Elasticsearch handles real-time search and analytics:
Sharded Architecture:
Data is distributed across hundreds of nodes, ensuring scalability for terabytes of transaction records.
Lucene Indexing:
Elasticsearch uses Lucene to enable full-text search and multi-field aggregations.
Aggregation Framework:
TStore leverages this framework to generate merchant insights (e.g., total sales) with near real-time speed.
2. Message Queues: Kafka and RabbitMQ
Kafka: The Courier of TStore
Kafka acts as the data pipeline, efficiently transporting entities across different components of the TStore ecosystem. It handles asynchronous tasks like data lake backups, payment notifications, and near real-time search indexing. This asynchronous approach frees up TStore’s core for real-time operations while Kafka reliably delivers data in the background.
RabbitMQ: The Safety Net
RabbitMQ serves as a backup if Kafka experiences latency or degradation. It reliably buffers pending messages until Kafka recovers, ensuring none get lost. In extreme cases, messages are directed to RabbitMQ’s dead letter exchanges (DLX) for separate processing, allowing for human intervention or alternative handling strategies.
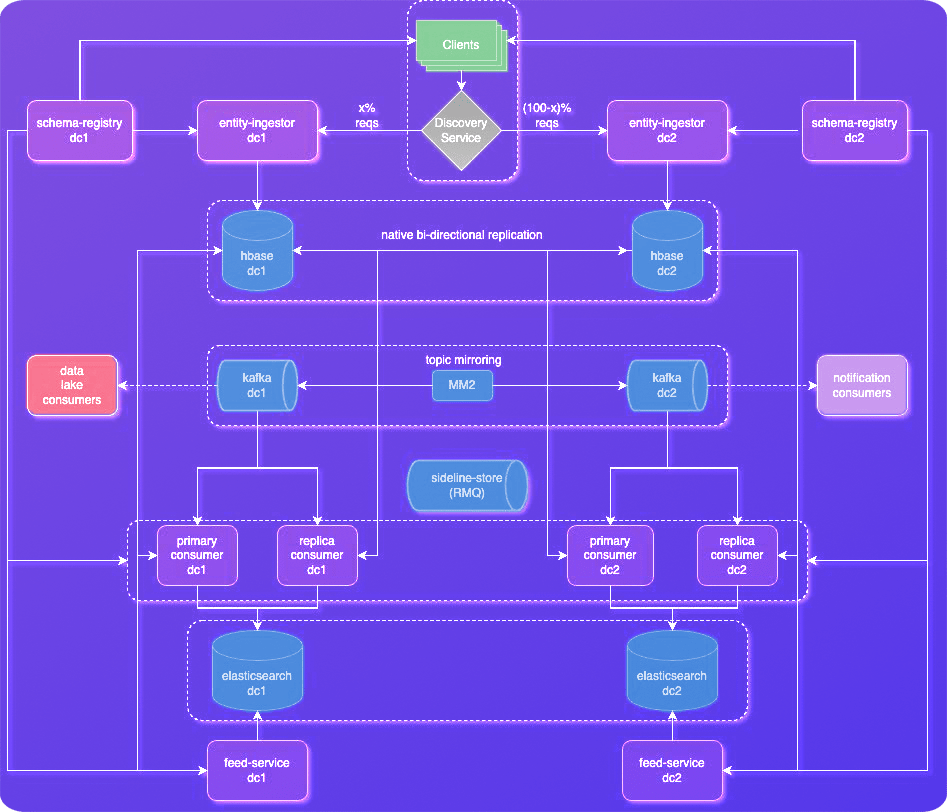
3. Disaster Recovery: Active-Active Architecture
In the high-stakes world of financial transactions, downtime is not an option. TStore incorporates a robust Active-Active Business Continuity and Disaster Recovery (BCP/DR) strategy to ensure uninterrupted transaction processing.
Active-Active Clusters: The Power of Two
TStore leverages geographically distinct Active-Active clusters, running two independent instances of the entire system in separate data centers. Both clusters handle read and write requests concurrently, eliminating single points of failure and guaranteeing service continuity. This design ensures:
Transactions continue processing even if one data center encounters an outage.
Data remains geographically separated, reducing the risk of regional disasters impacting both locations simultaneously.
Scalability is readily achievable by adding app and database instances to individual clusters as transaction volumes increase.
Seamless Data Synchronization: Replication and Mirroring
To maintain data consistency across both clusters, TStore employs various multi-leader data replication and mirroring mechanisms:
HBase Bi-directional Replication: Every write operation performed on one cluster triggers a replication stream to the other, ensuring identical data states in both locations.
Kafka Mirroring with MirrorMaker 2 (MM2): Continuously streams data topics from one Kafka cluster to the other, ensuring both clusters have identical, in-sync topics. This mirroring provides both read and write consistency across clusters.
Intelligent Traffic Shaping and Consistency Handling
The TStore client plays a crucial role in directing traffic and maintaining data consistency within the Active-Active setup:
Traffic Shaping: Routes writes to the appropriate cluster, balancing load and optimizing performance.
Out-of-Order Update Handling: Pins related updates together, ensuring they are always processed within the same cluster.
Failover and Recovery: Leverages manual intervention through Admin APIs to readjust request split and steer requests towards available and healthy clusters, prioritizing performance and business continuity.
4. Security and Privacy by Design
Views for Data Privacy
Views act as a protective layer, ensuring clients access only the fields they need while keeping sensitive information secure. For example:
A merchant view exposes only transaction amounts and payment statuses.
Personally Identifiable Information (PII) is excluded from all views.
Views improve network efficiency by minimizing data transfer, especially critical for TStore’s scale.
IAM for Access Control
TStore integrates with PhonePe’s in-house IAM platform, enforcing tenant-specific roles and permissions for every API call. This ensures that unauthorized access is impossible, even under edge cases.
Engineering Lessons from TStore
Whether you’re a student exploring system design or an engineer managing large-scale systems, TStore offers several key takeaways:
Polyglot Persistence: Use databases for what they do best—HBase for raw transaction storage, Elasticsearch for search and analytics.
Asynchronous Workflows: Offload non-critical tasks to message queues to ensure real-time performance.
Active-Active Resilience: Design for failure. Distributed systems must assume outages and plan accordingly.
Data Privacy by Default: Always restrict data access to the minimum required for business needs.
Closing Thoughts
TStore is more than a transactional system—it’s a testament to the art and science of engineering for scale, resilience, and efficiency. Its design empowers PhonePe to handle billions of transactions while ensuring security, reliability, and performance.
As TStore continues to evolve, it serves as a blueprint for the next generation of financial systems, inspiring engineers to push the boundaries of what’s possible.
The next time you complete a payment with PhonePe, remember the intricate machinery of TStore working tirelessly in the background, ensuring every transaction is swift, secure, and seamless.
References:
https://tech.phonepe.com/demystifying-tstore-the-backbone-of-billions-of-transactions-at-phonepe-chapter-2/
https://tech.phonepe.com/demystifying-tstore-the-backbone-of-billions-of-transactions-at-phonepe/