SD 2: Cracking the Code: What the Heck are JWT Tokens?
Hey there, future tech wizards! 👋 Ever wondered how websites remember who you are without asking for your password every single time? Or maybe you've heard the term "JWT tokens" thrown around in your coding classes and thought, "What in the world are those?" Well, buckle up, because we're about to dive into the fascinating world of JSON Web Tokens (JWTs)!
The Authentication Dilemma
Imagine this: You're building the next big social media app (move over, Zuckerberg!). How do you make sure that when Alice logs in, she sees her cat photos and not Bob's dog videos? 🐱🐶
This is where authentication comes into play.
🤔 Quick Question: What's the first solution that comes to your mind? Take a moment to think about it!
If you thought about using cookies, you're on the right track! Cookies have been the go-to solution for a while. But as the web evolves, we need something more flexible and powerful. Enter JWT tokens – the cool new kid on the authentication block!
The Traditional Cookie Approach: A Quick Recap
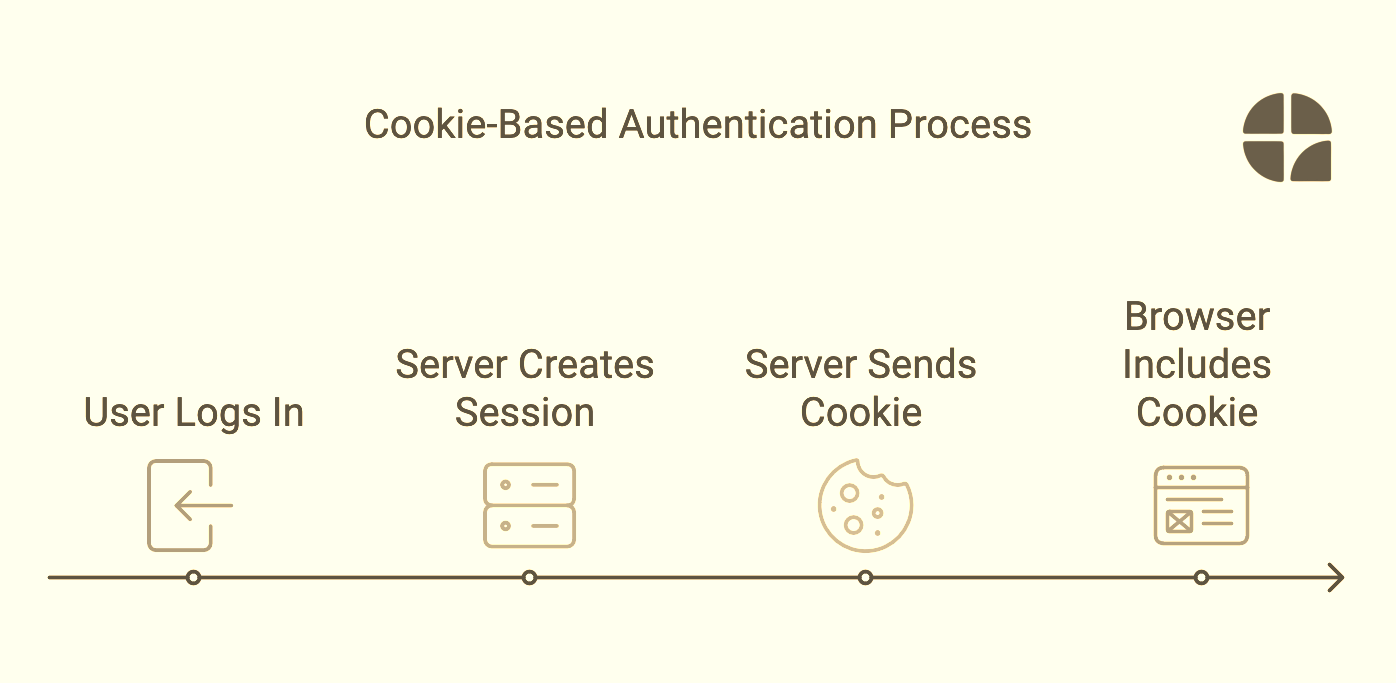
Before we dive into JWT tokens, let's take a quick trip down memory lane and revisit how cookies work. Imagine you're at a fancy tech conference, and here's how they might handle your registration:
🎟️ Cookie Authentication: The Conference Analogy
Registration (Login): You arrive and give your name at the reception.
Cookie Creation: They give you a special wristband with a unique code.
Server-side Storage: The reception keeps a record of your name and wristband code.
Subsequent Visits: Every time you enter a room, you show your wristband.
Verification: Staff checks with reception if your wristband is valid.
Access Granted: If valid, you're allowed to enter.
Now, let's break this down in tech terms:
🖥️ Server-side Session Storage
┌─────────────────────┐
│ Session ID | User │
├─────────────────────┤
│ ABC123 | Alice │
│ XYZ789 | Bob │
└─────────────────────┘🧠 Quick Quiz: Can you guess why this might be problematic for websites with millions of users?
The server needs to store session information for every single user. As the number of users grows, this requires more and more server memory and can slow down the authentication process.
Issues with Cookie-based Authentication:
Server Memory Overload: Imagine trying to keep track of wristbands for millions of conference attendees!
Scalability Challenges: What if the conference spreads across multiple buildings (servers)?
Single Point of Failure: If the reception desk (session storage) crashes, everyone's wristbands become useless.
💡 Fun Fact: Some large websites handle billions of logins per day. That's a lot of cookies to keep track of!
Now that we've refreshed our memory on cookies, are you ready to see how JWT tokens solve these problems? Let's dive in!
JWT Tokens: Your Digital VIP Wristband
Imagine you're at the hottest tech conference in town. At the entrance, instead of checking your ID every time you move between rooms, they give you a special wristband. This wristband has all the info they need about you – your name, which talks you can attend, even your favorite programming language!
That's essentially what a JWT token does in the digital world. It's like a secure, coded wristband for your web applications.
But What Exactly is a JWT Token?
JWT stands for JSON Web Token. Let's break it down:
JSON: You know this one! It's that neat format we use to structure data.
Web: Because, duh, we're using it on the web!
Token: A piece of data that represents something else (in this case, a user's identity and permissions).
Put them all together, and you get a secure way to transmit information between parties as a JSON object. Cool, right?
🚀 Interactive Moment: Go to jwt.io and look at the structure of a JWT token. Can you identify the three main parts? (Hint: They're separated by dots!)
The Anatomy of a JWT Token
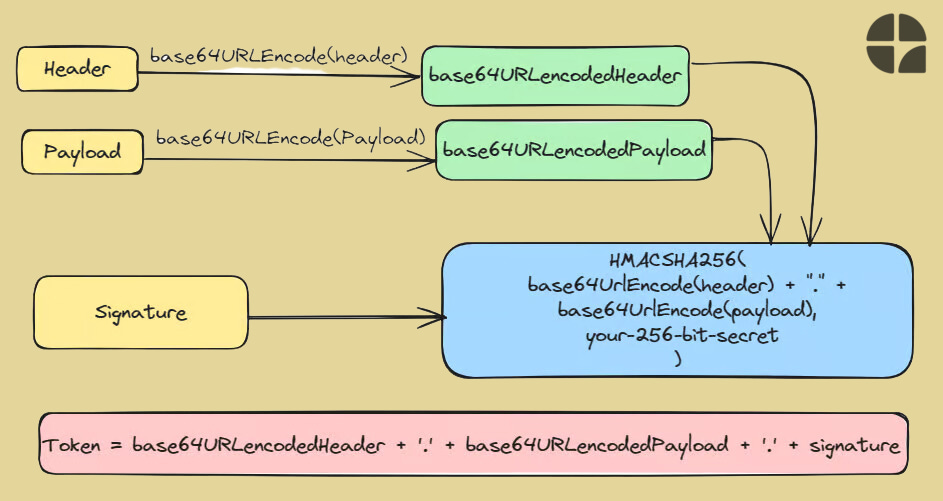
Every JWT token has three parts:
Header:
The header contains the data about the token itself. It is mainly used to give information about the signing/decryption technique used on it.
It can also hold key information about the media or content type of the transmitted data. All this information is present as a JSON object, then this JSON object is encoded to BASE64URL.
Payload:
It can contain any data related to your system. Basically, it can have the data you want to feed in, i.e. it may include the user's ID with a list of features they can interact with.
The information is presented as key/value pairs, and the keys are called "claims" in JWT. Even this is encoded to BASE64URL.
Signature:
A signature is used to verify the authenticity of the token. It ensures that the token hasn’t been altered along its way.
The signature of a JSON Web Token is created using the BASE64URL encoded header and payload which are joined together with dot(.) which is further hashed using the hashing algorithm mentioned in the header with a secret key.
These parts are each encoded and concatenated with dots, looking something like this:
[header].[payload].[signature]
xxxxx.yyyyy.zzzzzWhere xxxxx is the encoded header, yyyyy is the encoded payload, and zzzzz is the signature.
In reality, it looks like this (I know 🤮)
eyJhbGciOiJIUzI1NiIsInR5cCI6IkpXVCJ9.eyJzdWIiOiIxMjM0NTY3ODkwIiwibmFtZSI6IkpvaG4gRG9lIiwiaWF0IjoxNTE2MjM5MDIyfQ.SflKxwRJSMeKKF2QT4fwpMeJf36POk6yJV_adQssw5cDon't worry; you don't need to memorize this! 😅
Real-World Use Cases of JWT Tokens
Now that we understand what JWT tokens are, let's explore where they shine in the real world. Imagine you're building the next big tech startup – here's how you might use JWTs:
🔐 1. Single Sign-On (SSO)
Scenario: Your startup has multiple services (email, project management, chat).
How JWTs Help: Users log in once and get a JWT that works across all services.
🤔 Think About It: How many times do you log into Google to use Gmail, YouTube, and Google Drive?
🌐 2. Authentication in Microservices
Scenario: Your app is built with microservices architecture.
How JWTs Help: Each microservice can verify the JWT without calling a central auth service.
┌─────────┐ JWT ┌─────────┐
│ User │ ─────────▶ │ Service │
│ Service │ │ A │
└─────────┘ │ └─────────┘
│ │
│ │ ┌─────────┐
│ └────▶ │ Service │
│ │ B │
▼ └─────────┘
No central auth
service needed!📱 3. Mobile App Authentication
Scenario: You're developing both web and mobile versions of your app.
How JWTs Help: Mobile apps can easily store and send JWTs with each request.
🔁 4. API Authentication
Scenario: You're offering a public API for developers.
How JWTs Help: Developers can use JWTs to authenticate their requests to your API.
👨💻 Coding Challenge: Can you think of a popular API that uses JWT for authentication? (Hint: Think social media platforms)
Twitter's API uses OAuth 2.0, which often involves JWTs for token-based authentication.
🔄 5. Stateless Session Management
Scenario: You want to scale your app without worrying about session storage.
How JWTs Help: All session info is in the token – no need to store sessions on the server!
🚀 Pro Tip: While JWTs are powerful, they're not a one-size-fits-all solution. Always consider your specific security needs and potential trade-offs!
Now that we've seen where JWTs are commonly used, can you think of an app or service you use daily that might be using JWTs behind the scenes? Share your thoughts!
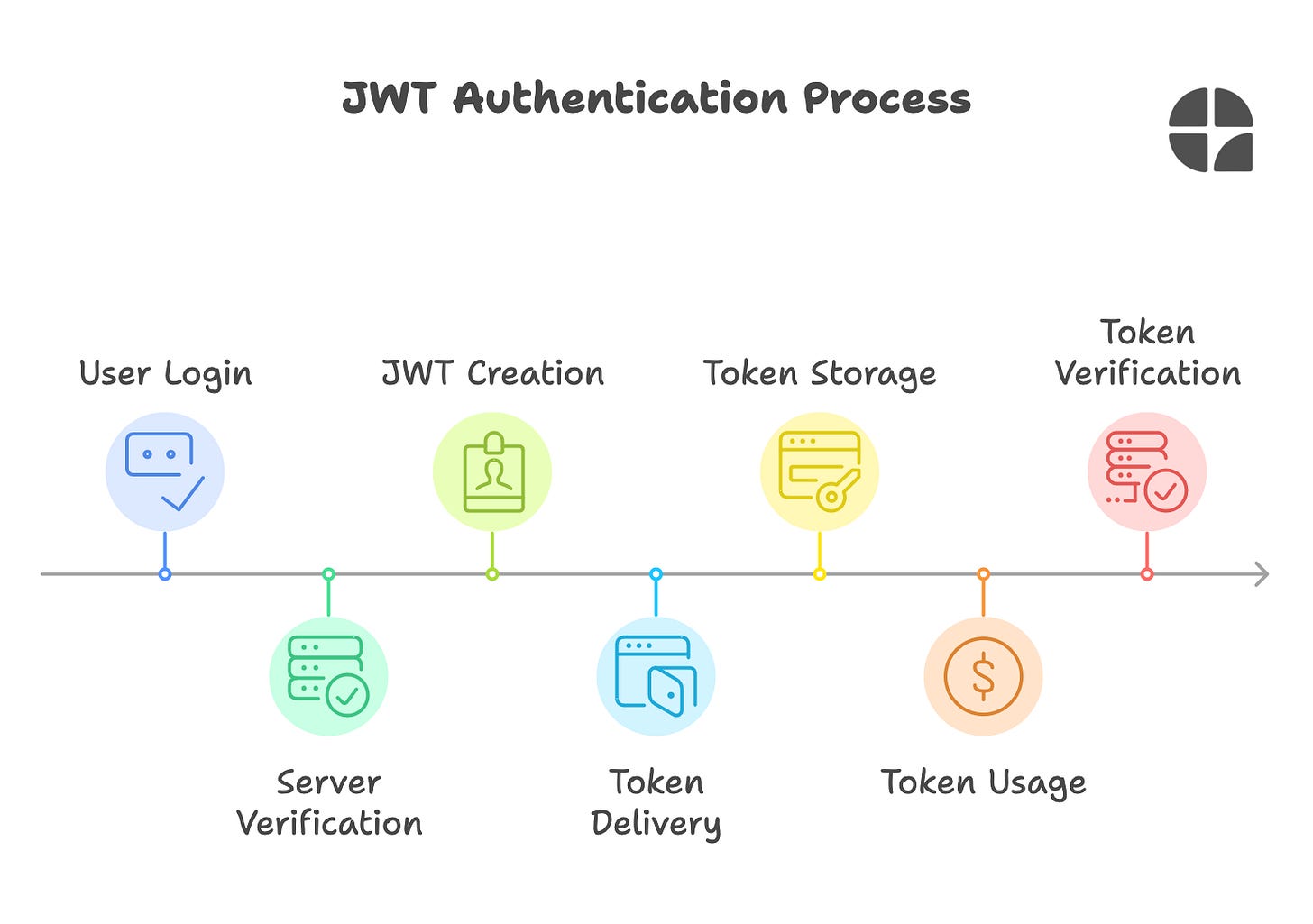
How JWT Works: A Step-by-Step Adventure
You log in with your username and password
The server verifies your credentials
If correct, the server creates a JWT token with your info
The server sends this token back to your browser
Your browser stores the token (usually in local storage)
For future requests, your browser sends this token along
The server verifies the token's signature and grants access if valid
🤯 Mind-Blowing Fact: The server doesn't need to store session information for each user. The token itself contains all the necessary info!
Why Are JWTs So Cool?
Stateless: Servers don't need to keep track of sessions.
Scalability: Great for distributed systems and microservices.
Security: Can be encrypted and signed.
Flexibility: Can include any type of claims or custom data.
Decentralized: Can be verified by multiple servers
But remember, with great power comes great responsibility! JWT tokens aren't a silver bullet for all security concerns.
⚠️ Security Tip: Never store sensitive info (like passwords) in the JWT payload. It's encoded, not encrypted!
Hands-On Time!
Let's create a simple JWT token:
Go to jwt.io.
Go to the "Debugger" section
In the "Payload" section, try adding your own claims. For example:
{
"name": "Your Name",
"role": "Awesome Developer",
"exp": 1735689600
}Watch how the token changes in real-time!
Challenge: Try changing the algorithm in the header from HS256 to RS256. What happens? Why do you think this change is significant?
Common Pitfalls and Best Practices
While JWTs are powerful, they're not a silver bullet. Here are some things to keep in mind:
Don't store sensitive info in the payload (it's base64 encoded, not encrypted!).
Use HTTPS to prevent token interception.
Set appropriate expiration times for your tokens.
Implement token refresh mechanisms for long-lived sessions.
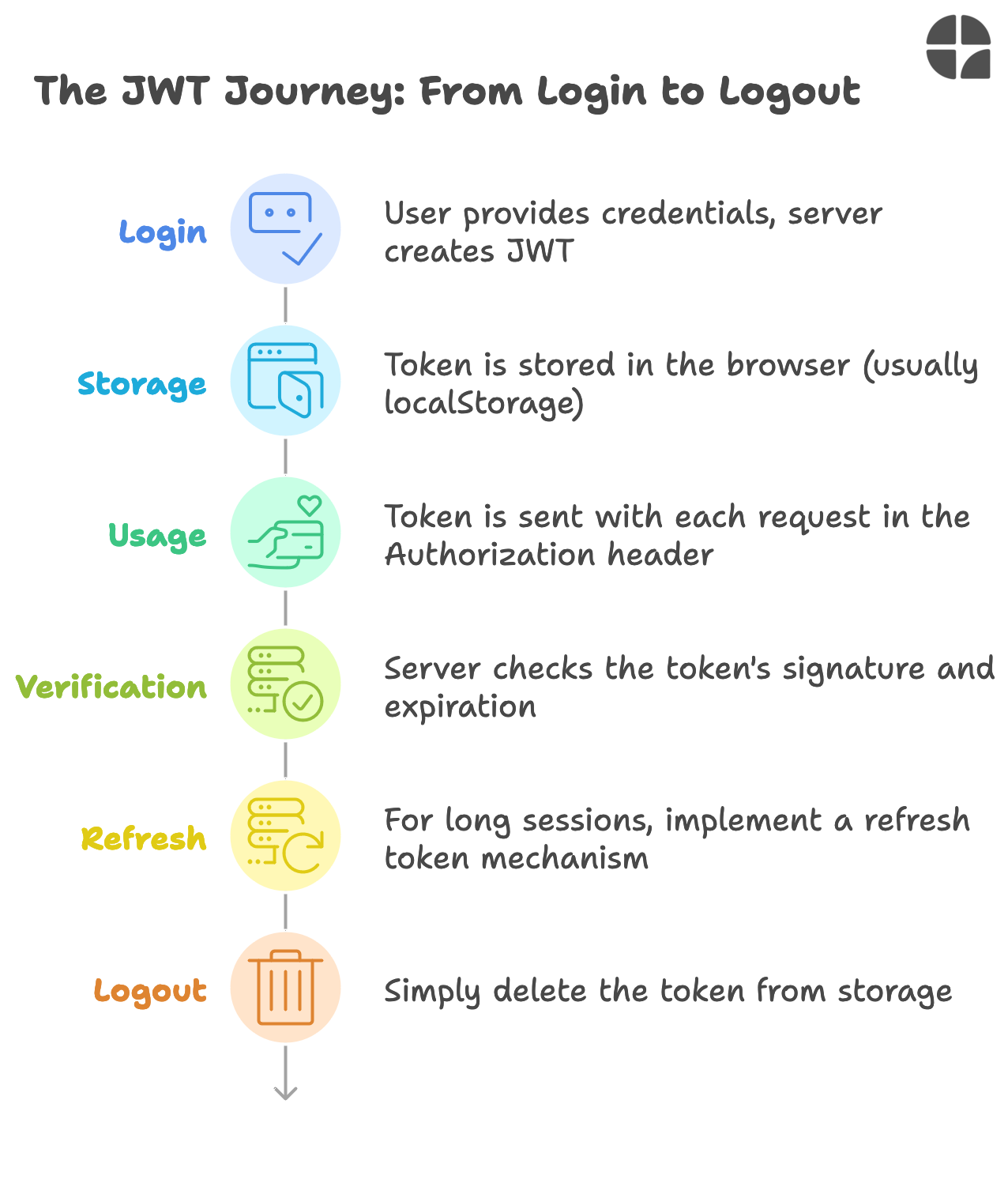
The JWT Journey: From Login to Logout
Login: User provides credentials, server creates JWT
Storage: Token is stored in the browser (usually localStorage)
Usage: Token is sent with each request in the Authorization header
Verification: Server checks the token's signature and expiration
Refresh: For long sessions, implement a refresh token mechanism
Logout: Simply delete the token from storage
🤯 Mind-Bender: How would you handle token expiration on the client-side? Think about user experience!
The Big Picture: JWTs in System Design
Understanding JWTs is crucial for modern system design, especially when building scalable, distributed systems. They solve many authentication and authorization challenges in microservices architectures.
🤔 Food for Thought: How might JWTs change the way you approach session management in your next project?
Wrapping Up
Congratulations! You've just unlocked the mystery of JWT tokens. From understanding their structure to grasping their role in modern web applications, you're now equipped with knowledge that's crucial for any aspiring system designer or web developer.
Quick Recap:
JWTs are like digital wristbands for web apps.
They consist of a header, payload, and signature.
JWTs enable stateless authentication, improving scalability.
Always use them securely and never store sensitive data in them. Final Challenge: Think about an app you use daily. How might it be using JWTs behind the scenes? Can you spot any potential security improvements?
🚀 Next Steps:
Implement JWT authentication in a small project
Explore libraries like jsonwebtoken for Node.js
Research best practices for JWT token storage and security
Remember, the world of web development is constantly evolving, and understanding concepts like JWTs puts you ahead of the curve. Keep exploring, keep coding, and who knows? Maybe you'll be the one designing the next big authentication system!
Got questions? Excited to use JWTs in your next project? Drop a comment below and let's keep the conversation going! 🚀💻
Recommended Reads for Your Journey
Explore these highly recommended books to deepen your knowledge in System Design, Software Engineering, and Coding:
Designing Data-Intensive Applications by Martin Kleppmann
A must-read for understanding distributed systems and modern data engineering.
Buy hereSystem Design Interview – An Insider's Guide by Alex Xu
Perfect for preparing for system design interviews with practical case studies.
Buy hereClean Code: A Handbook of Agile Software Craftsmanship by Robert C. Martin
Learn how to write code that is readable, maintainable, and efficient.
Buy hereThe Pragmatic Programmer: Your Journey to Mastery by Andy Hunt and Dave Thomas
A timeless guide for becoming a well-rounded software developer.
Buy hereOperating Systems: Three Easy Pieces by Remzi H. Arpaci-Dusseau and Andrea C. Arpaci-Dusseau
Dive deep into the fundamentals of operating systems.
Buy here